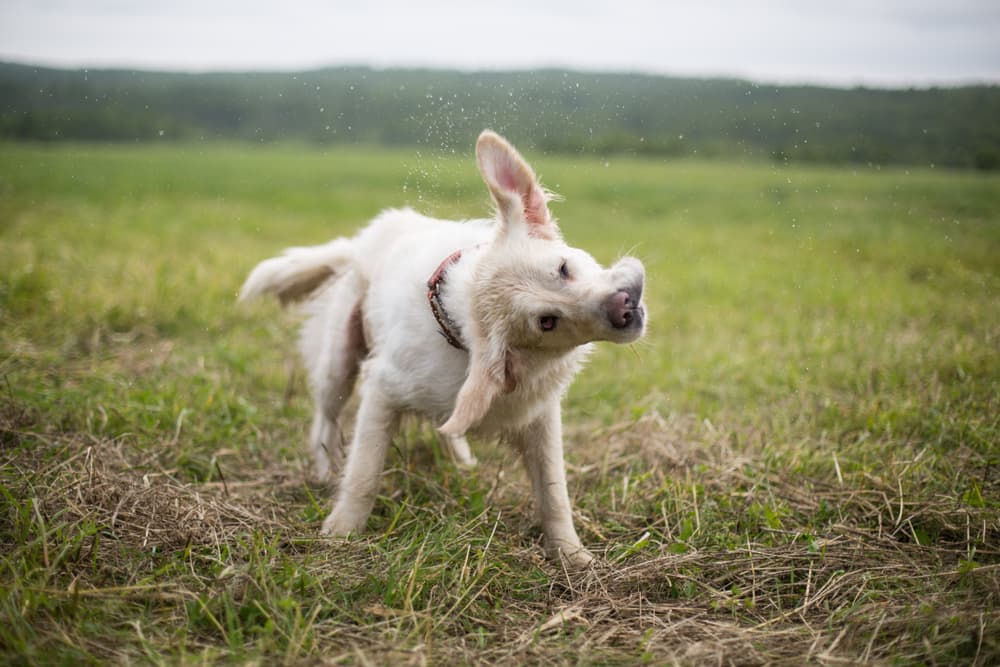
You ’re lying in bed after a long day at body of work , seek to fall numb . Just as you take off to be adrift off , you ’re startled awake by the jingling of collar tags as your dog shakes his head . After shaking for a few second , your dog finally finalize down , and so do you … until the next round of headway shake starts up again .
This pattern repeats again and again , every few minutes . As the night wear on , your annoyance plough to fear and you begin to worry about what could be do this behaviour .
understand on to learn more about why dogs shake their heads , and what you could do to help .

Why Do Dogs Shake Their Heads?
frump shake their brain for a potpourri of reasons , and it is n’t always an abnormal doings . In some contexts , head shaking is entirely predictable and expect . Many dogs shake their heads when they first wake up , just like we run to stretch when we get out of bed .
Dogs also tend to excite their heads when they ’re playing with a toy or excited . Some dogs even do a full - eubstance handshaking , start at the head teacher and widen all the way of life along the body to the tail . They might also shake their heads if they get wet from a bathroom or from swim . An occasional shake of the head is nothing to be concerned about .
unreasonable promontory shake up , however , often has an implicit in medical cause . If your hot dog is repeatedly and frequently shake their point , especially if this is a change from their normal demeanor , it ’s significant to square off the effort of their unnatural head shake .

Why Does My Dog Keep Shaking His Head?5 Potential Reasons
The most common cause of unnatural nous shaking in dogs is inflammation of the capitulum , shout otitis . There are several likely cause of otitis , each of which differ in their treatment and long - terminal figure direction . have ’s explore them further .
Ear Infection
Ear infections are a comparatively common problem in dogs . They fall out when bacteria oryeast(which are always present in the environment ) proliferate to an extravagant level within the ear epithelial duct . Infection can occur in the internal , middle , or outside ear canal , although infections of the outside ear duct ( otitis externa ) are the most mutual in dog-iron . Factors that may predispose a wiener to develop otitis externa admit overweening wet in the ear canal , allergies , and endocrine disease ( such as hypothyroidism ) .
Ear Mites
Ear mitescan cause inflammation of the capitulum , but they are really relatively uncommon in grownup dogs . They are more common in puppies , peculiarly those house in a crowded situation that promote snug contact with other domestic dog . spike jot are microscopic parasites that inhabit within the spike canal , do severe annoying and uncomfortableness for affected dogs .
Foreign Body
extraneous objects , such as pasturage seeds , occasionally find their way into a dog ’s pinna canal . If this occurs , they may cause substantial irritation and inflammation , get a bounder to throw off their head and show other preindication of discomfort .
Ear Trauma
Any wound to the ear can cause irritation and head shake . Trauma can have an outside seed ( such as a bite combat injury from another pawl ) , or it may be triggered by ego - harm ( a dog that scratches their ear and stimulate an injury with their toenail ) .
Allergic Otitis
If a hound is shaking their promontory with no capitulum infection or other seeable irregularity , allergies may be to blame . Many weenie are allergic to inhaled allergens , such as tree pollen , Mary Jane , grasses , mould , etc . Other dogs are allergic to proteins within their solid food , such as beef or chicken . Both type of allergic reaction can lead to fervour within the ear canals .
Other Causesof Dog Head Shaking
While ear infection , ear speck , foreign physical structure , ear trauma , and hypersensitive otitis are certainly the most coarse causal agent of head shake in dogs , there can be other crusade .
Any disease that affects the auricle , include rarefied autoimmune disorder and generalized skin issues , can run to shaking of the head .
In rarefied cases , your dog ’s head shaking may even have a cause other than capitulum or tegument disease . Determining the cause of your cad ’s head escape from requires a thorough veterinary workup .
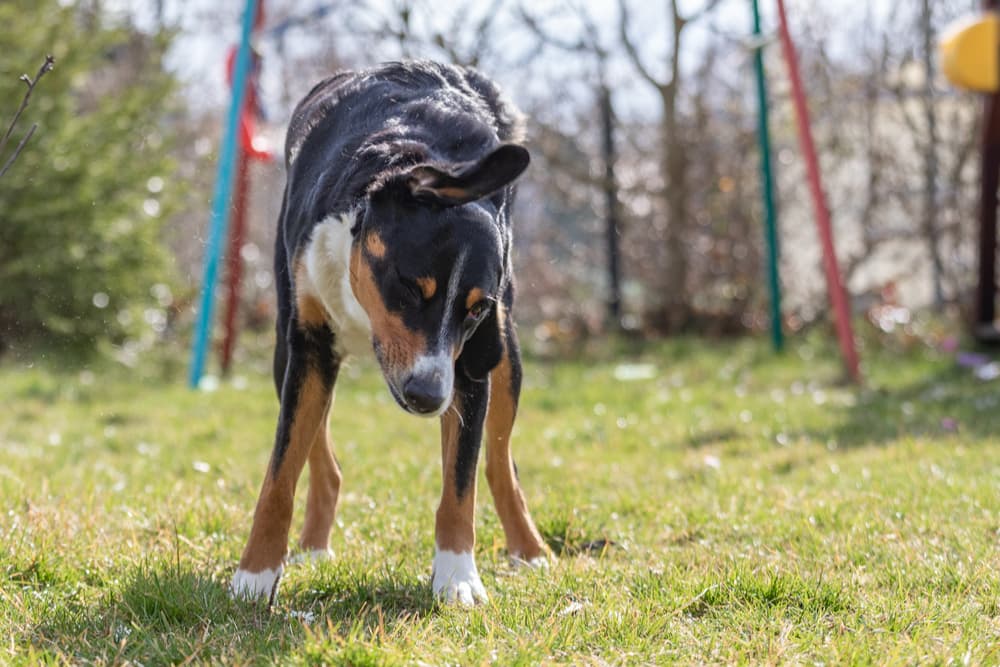

What to Do if Your Dog Keeps Shaking His Head
A new attack of persistent head judder in a dog should incite a sojourn to the veterinarian . You do n’t necessarily call for to hotfoot to the emergency veterinarian flop away , because a single sequence of head shake off could have a soft cause ( like an dirt ball morsel ) . If the head shaking persists , however , you will desire to have your dog essay within the next one to two days .
A frankfurter that shake their head forcefully and for a prolonged period of clip can actually damage their ear . Blood vessel in the ear can burst , filling the pinna ( ear fluttering ) with blood and lead in a condition called anaural hematoma(ear hematoma ) , which is a profligate blister . The pinnae can also become damage by the force with which they hit your dog ’s head and neck , top to scabs and wound on the ear .
If your dog ’s head shaking is make by an ear contagion , early treatment is more effective and will run to more rapid resolution . delay treatment will not only prolong your cad ’s soreness , it could also make your dog ’s auricle infection more challenging and expensive to plow .
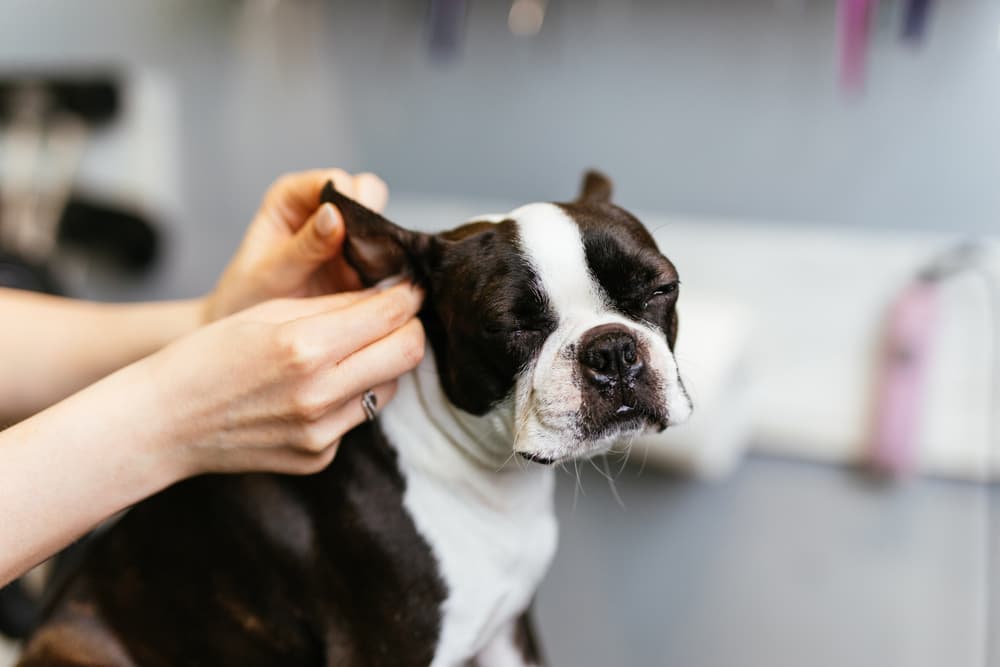

Dog Shaking Head:Diagnosis and Treatment
Your veterinary surgeon will likely begin by do a thorough physical exam , looking for any other sign of illness or disease . Next , your veterinarian will focus on your dog ’s ear . They will soundly examine your dog ’s pinnae ( external ear flap ) , reckon for wounds , inflammation , and other abnormalcy . Next , they will perform an otoscopic test , in which an otoscope ( an legal instrument designed to permit rating of the ear canal ) is used to leave a magnify thought of your hound ’s ear canals and ear drum . The otoscopic exam will tolerate your veterinarian to look for excitation of the ear epithelial duct , dust in the auricle duct , and any abnormalities associated with the eardrum .
If your veterinarian go steady any evidence of otitis or otherwise suspect a condition affect your heel ’s ears , an auricle cytology will belike be recommended . This test involves remove a small sample of debris from the capitulum epithelial duct with a cotton fiber swob , and then examining that rubble under the microscope . An ear cytology can tell your veterinarian whether your dog has ear mites , a bacterial infection , or a yeast transmission within the ears . If inflammatory cells are found in the absence of an infection , this can suggest the comportment of sensitised redness .
Once your veterinarian has determined the cause of your dog ’s ear ignition , handling will be order . Most ear infections are treat with prescription medicine ear cleaners and topical medications . Oral medications may also be prescribed , especially in dogs with underlying allergy .

Some topical medications are applied by a veterinary surgeon in the veterinary clinic . This alleviates the hassle of you take you medicate your dog ’s capitulum at base , but necessitate you to return for adopt - up treatments every one to two weeks until the transmission has resolve . Other treatments are designed to be administer by a dog ’s owner at home , once or twice daily . Your veterinarian will mouth to about which discussion is best for your dog , and give you instructions for complete your dog ’s course of treatment . If necessary , a veterinary technician may demonstrate how to strip and medicate your dog ’s auricle . A recheck date will likely be schedule , so your veterinary surgeon can insure that the contagion has solve .
If your dog ’s otoscopic exam and ear cytology do not show any grounds of otitis , your vet will let the cat out of the bag to you about further recommended examination to find out the cause of your dog ’s head shaking .
Related condition